What Is EHS in Healthcare and Why It Matters for Patient and Worker Safety

Healthcare facilities rely on safe air, controlled environments, and strong safety practices to protect the people inside them. When any of these systems falter, the consequences can be serious. According to the Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, about 1 in 31 hospital patients develops at least one healthcare-associated infection on any given day. Many of these infections are influenced by environmental conditions, air handling, waste management, and the everyday safety practices that EHS programs help control.
Environmental Health and Safety, or EHS, provides the structure that healthcare organizations use to reduce these risks. It brings together environmental protection, worker health, and workplace safety to support consistent, high-quality patient care. Understanding what EHS means is essential for anyone who manages clinical spaces, oversees facility operations, or works in environments where patients depend on safe, well-regulated conditions.
In this guide, we’ll help you understand what is EHS, why it matters in healthcare, and the core elements every facility should have in place to protect both patients and staff.
What Is EHS?
Environmental Health and Safety, or EHS, is the system organizations use to manage environmental responsibilities, protect workers, and maintain safe conditions throughout the workplace. It brings together the practices, training, and oversight needed to reduce risks and support a healthy work environment.
When people ask “what does EHS mean?”, the simplest answer is that it is a framework that helps workplaces control hazards before they cause harm. In many industries, EHS supports areas like waste handling, chemical safety, air quality testing, and injury prevention.
In healthcare settings, these responsibilities extend even further. EHS programs help protect the controlled environments patients rely on by supporting safe waste management, proper ventilation, exposure control, and the overall safety practices that keep clinical spaces functioning smoothly.
The Three Parts of EHS
Environmental Protection
Environmental protection focuses on how a facility interacts with the world around it. This includes managing waste correctly, preventing pollution, storing chemicals responsibly, and maintaining systems that protect air and water quality.
Strong environmental oversight ensures a facility follows the laws and standards designed to limit environmental impact. Examples include proper hazardous waste labeling, stormwater protection measures, routine air sampling, and spill prevention planning. Facilities also rely on environmental monitoring to confirm that exhaust, emissions, or discharges stay within regulatory limits.
While healthcare has unique waste streams and stricter expectations, the fundamentals remain the same. Environmental protection ensures a facility operates responsibly, avoids contamination, and maintains compliance with EPA and state environmental rules.
Workplace Health
Workplace health focuses on the conditions that influence worker well-being. This includes exposure control, air quality assessments, ergonomic practices, and the preventive measures that limit long-term health risks.
A strong workplace health program identifies hazards early. It evaluates chemical risks through Safety Data Sheets, monitors noise and ventilation levels, and uses industrial hygiene testing to detect airborne contaminants. Facilities also build programs to reduce strain injuries, support respiratory protection, and conduct routine health surveillance where required.
These efforts reduce the likelihood of chronic exposure, acute illness, or long-term occupational injury. When workplace health is supported consistently, teams work more safely and with fewer disruptions.
Safety Standards
Safety standards guide the day-to-day practices that keep workers safe from physical injury. This covers equipment use, machine guarding, safe work procedures, emergency response steps, and the training workers need to perform tasks without unnecessary risk.
Organizations develop safety plans that outline responsibilities, inspection schedules, incident reporting methods, and the controls used to prevent injuries. Personal protective equipment, ladder safety training, lockout programs, and fall protection are all common examples of how facilities meet OSHA expectations and reduce the likelihood of accidents.
Strong safety standards promote consistent habits across teams. They reduce unplanned downtime, provide clarity in high-risk situations, and reinforce a culture where every worker understands how to complete tasks safely.
Why EHS Matters for Every Workplace
Upper management support is essential for EHS programs to succeed in the long term. When leaders visibly prioritize safety and environmental responsibility—through resource allocation, clear expectations, and consistent participation—it signals that EHS is a core business value, not just a compliance task. By embedding EHS into decision-making, performance goals, and employee behaviors, organizations create a culture in which safety and environmental awareness are integral to how work is done at every level, rather than a separate or reactive effort.
Employee involvement is essential to an effective EHS program because those closest to the work are often the first to identify hazards and opportunities for improvement. By encouraging reporting, near-miss sharing, and shared accountability, organizations reinforce that EHS is a collective responsibility across all roles—not the sole responsibility of a single department.EHS programs play a critical role in maintaining safe and well-regulated workplaces. They help organizations identify risks early, put controls in place, and create consistent practices that prevent injuries and environmental harm. When EHS systems function well, they reduce disruptions, improve reliability, and support a healthier workforce.
A strong EHS program also helps organizations meet the regulatory expectations that guide how facilities operate. This includes OSHA safety requirements, environmental regulations, and industry-specific standards. Staying compliant protects employees and the environment while also reducing the likelihood of fines, enforcement actions, or operational shutdowns.
EHS programs contribute to financial stability as well. Fewer injuries mean fewer workers’ compensation claims. Better waste handling and chemical management lower cleanup costs and prevent incidents that can halt operations. When employees work in safer environments, productivity increases and turnover tends to decline.
Trust is another important outcome. Employees, customers, and community members pay attention to how organizations manage safety and environmental responsibility. A visible commitment to EHS builds confidence and supports a reputation of reliability and professionalism.
Environmental Health and Safety is more than a set of rules or inspections—it is an integrated approach to protecting people, the environment, and organizational operations. When leadership support, employee involvement, and continuous improvement come together, EHS becomes part of the organization’s culture rather than a standalone function. Across healthcare, manufacturing, and corporate environments, strong EHS programs reduce risk, support compliance, and create safer, more resilient workplaces where people and processes can perform at their best.

Core EHS Elements That Matter Most in Healthcare Facilities
Infection Control and Prevention
Preventing the spread of infection is central to patient and worker safety. EHS teams support infection control by ensuring the environment remains clean, well-ventilated, and compliant with hospital sanitation standards.
Key responsibilities include:
- Supporting proper surface disinfection and cleaning practices
- Ensuring sterilization processes align with facility protocols
- Monitoring air quality and ventilation performance
- Coordinating safe handling and disposal of infectious waste
- Verifying that isolation spaces and containment areas function as intended
Readers who want deeper guidance on containment systems can explore HigginsEDU's article on American Society for Health Care Engineering's (ASHE) updated Infection Control Risk Assessment (ICRA 2.0), which outlines evolving expectations for infection prevention in healthcare construction.
Hazardous Materials and Medical Waste Management
Hospitals generate a wide range of materials that require careful handling. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, more than 3.5 million tons of medical waste are produced each year in the United States. Much of this waste must be segregated, contained, and treated using strict procedures to prevent environmental contamination and worker exposure. EHS programs help ensure these materials are managed safely and in accordance with regulatory requirements.
Typical areas of oversight include:
- Proper storage and labeling of chemicals and pharmaceuticals
- Tracking and managing hazardous drug waste, sharps, and biohazard materials
- Ensuring waste is segregated correctly before disposal
- Training staff on spill response procedures
- Maintaining compliance with EPA, OSHA, and state medical waste rules
Poor handling in any of these areas can lead to environmental contamination or worker exposure, making this a critical EHS function.
Employee Safety and Exposure Control
Healthcare workers face several occupational risks that other industries do not encounter. EHS programs help reduce these exposures and create safer working conditions.
Examples of exposure control responsibilities:
- Training staff on proper PPE use and maintenance
- Supporting bloodborne pathogen programs and compliance
- Reducing needlestick and sharps-related injuries
- Managing chemical exposure risks in labs, pharmacies, and clinical departments
- Improving ergonomic conditions to reduce strain and musculoskeletal injuries
Worker protection in these areas becomes even more important when combined with the ventilation and exposure risks present in clinical environments.
Indoor Air Quality and Ventilation Compliance
Indoor air quality is a foundational part of environmental and worker protection, especially in clinical environments where airborne transmission risks are high. Airflow and ventilation directly influence infection control and overall patient safety. Hospitals depend on systems that maintain consistent pressure relationships, filter airborne contaminants, and support healthy air exchange rates.
Key ventilation and air-quality EHS tasks include:
- Monitoring isolation room airflow and maintaining required pressure levels
- Assessing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) performance and verifying proper filtration
- Conducting industrial hygiene testing for gases, chemicals, and airborne pathogens
- Ensuring construction and maintenance activities do not disrupt clean-air zones
- Supporting compliance with facility guidelines and regulatory expectations
Clean, well-managed air systems help protect patients recovering from illness and staff who work long shifts in clinical environments. For a deeper look at negative-pressure system performance, HigginsEDU’s guide to HEPA air filter blower testing provides practical steps for evaluating HEPA-filtered exhaust systems.
Emergency Preparedness for Healthcare Settings
Hospitals must be ready to respond quickly when an emergency threatens patient care. EHS teams help facilities plan for events that could disrupt operations or create safety hazards.
Common emergency preparedness responsibilities include:
- Developing evacuation routes and safety procedures for patient populations
- Coordinating plans for power outages, equipment failure, or utility disruptions
- Preparing spill response procedures for chemicals or hazardous materials
- Supporting infectious disease response plans and surge protocols
- Conducting drills and coordinating with local emergency services
Strong preparedness ensures staff know what to do during an emergency and helps maintain patient safety even under pressure.
Supporting Compliance with the Joint Commission
EHS programs play a critical role in helping healthcare organizations meet The Joint Commission’s Environment of Care (EC) and Life Safety (LS) standards. Many Joint Commission requirements—ranging from infection prevention and hazardous materials management to emergency preparedness and air quality—are directly supported by strong EHS oversight and documentation.
Through routine inspections, risk assessments, training, and performance monitoring, EHS teams help facilities demonstrate compliance with Joint Commission expectations for maintaining a safe, functional, and compliant care environment. This includes supporting readiness for surveys, addressing findings through corrective action plans, and ensuring environmental controls consistently protect patients, staff, and visitors. When EHS is well integrated into daily operations, organizations are better prepared to meet accreditation requirements and sustain compliance between survey cycles.
When these core elements work together, they create a safer, more reliable environment for both patients and staff.
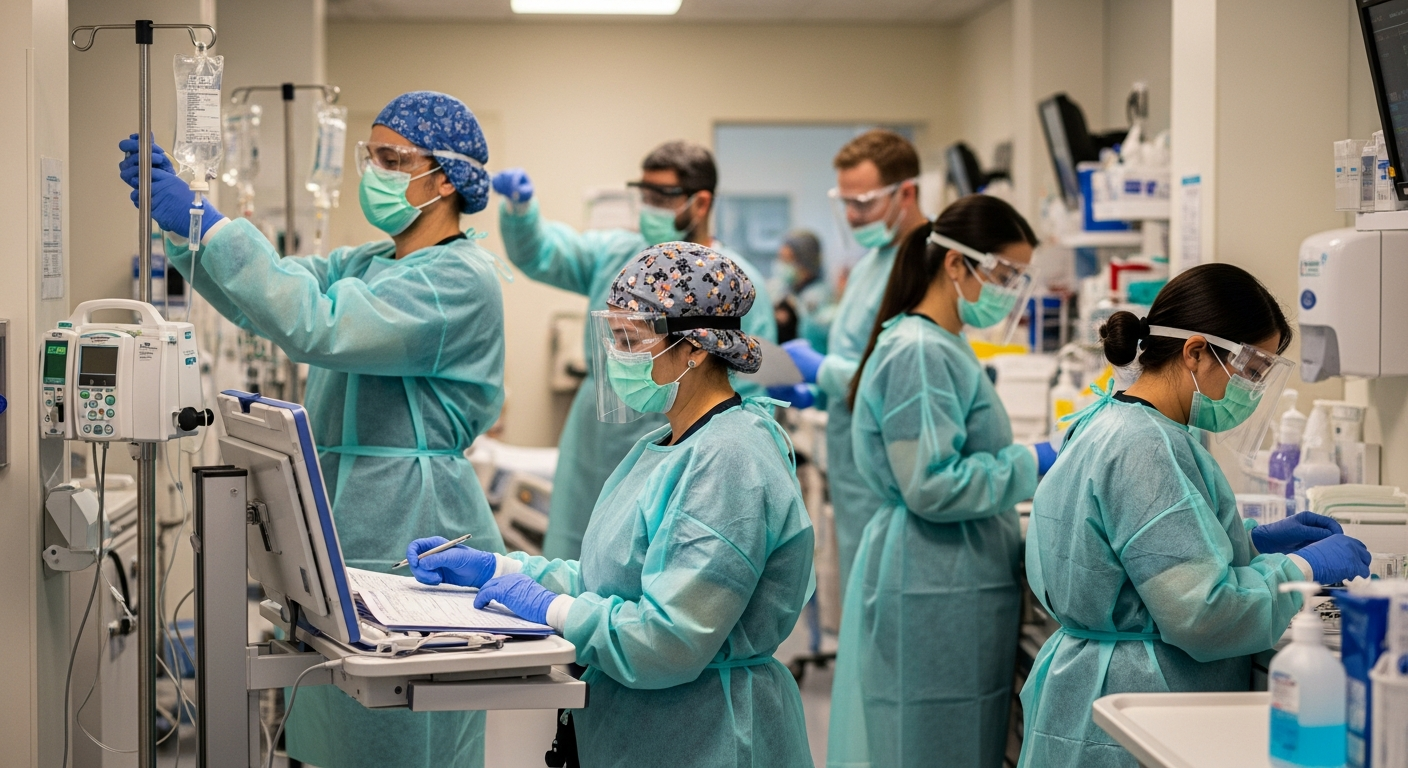
Benefits of a Strong EHS Program in Healthcare
Better Patient Safety and Care Quality
Good EHS practices help create clean, well-controlled environments that support better patient outcomes.
Key impacts include:
- Lower risk of environmental and airborne transmission
- Fewer hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) linked to poor sanitation, ventilation, or material handling
- More consistent hygiene and workflow practices across departments
- Cleaner air and surfaces that support healing and recovery
Patients rely on safe surroundings during treatment. Strong EHS programs help reduce the environmental factors that can interfere with care.
Protection for Healthcare Workers
Clinical staff, support teams, and contractors face exposures unique to healthcare settings. A comprehensive EHS program helps reduce these risks and ensures workers have the training and resources they need.
Common benefits include:
- Lower rates of needlestick injuries and sharps exposure
- Reduced contact with hazardous chemicals and disinfectants
- Better control of airborne hazards and respiratory risks
- Improved ergonomics and safer patient-handling practices
- Greater awareness of personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements and safety procedures
A safer workforce is a more stable workforce. When people feel protected, stress and burnout decrease and job satisfaction increases.
Stronger Compliance With Healthcare Regulations
Healthcare facilities must follow a wide range of environmental and safety regulations. A strong EHS program provides the structure needed to stay compliant with expectations from:
- OSHA
- Joint Commission standards
- EPA and state environmental agencies
- Medical waste and hazardous materials rules
- Infection control and ventilation requirements
Consistent compliance helps facilities avoid citations, fines, or operational interruptions. It also reinforces trust among patients, auditors, and accreditation bodies.
Reduced Operational Costs and Liability
Preventing incidents is always less expensive than responding to them. Effective EHS programs help facilities:
- Reduce workers’ compensation claims
- Lower costs related to spills, exposures, or waste mismanagement
- Avoid disruptions caused by equipment failure, unsafe conditions, or regulatory issues
- Minimize legal risks connected to patient or worker harm
Over time, these savings can be significant. EHS is both a protective measure and a smart financial strategy.
Improved Reputation and Trust
Safety, cleanliness, and environmental responsibility influence how patients and communities view a healthcare facility. Hospitals known for strong safety practices tend to attract more trust and maintain better relationships with patients and partners.
A visible commitment to EHS helps facilities demonstrate:
- Transparency
- Professionalism
- Care for patient and worker well-being
- Strong operational standards
Reputation is not built overnight, but consistent EHS performance strengthens it year after year.
How Higgins and Associates Supports EHS Programs
EHS Consulting and Training for Healthcare and Construction
Learn more about our EHS consulting for healthcare.
Environmental Assessments and Property Risk Services
Beyond healthcare, we assist clients with environmental evaluations for property transactions, redevelopment, and due diligence. These services help organizations identify hazards and make informed decisions before acquiring or renovating a site.
See our EHS services for property transactions and redevelopment.
No matter the industry, our goal is to help teams reduce risk, improve safety performance, and build environments that support healthy, compliant operations.
Final Thoughts
Environmental Health and Safety plays a defining role in how healthcare facilities protect patients, support their workforce, and maintain reliable, compliant operations. Understanding what is EHS helps leaders recognize how environmental controls, worker safety practices, and strong regulatory compliance all fit together to create safer clinical environments.
Because risks evolve over time, EHS programs should be reviewed regularly to confirm that procedures, documentation, ventilation systems, training, and waste-handling practices continue to meet current standards. Even small gaps in process can have meaningful impacts on patient outcomes and staff well-being.
For organizations that want to strengthen their programs, partnering with experienced EHS specialists can streamline that work and provide the technical guidance needed to maintain safe, high-performing facilities. Higgins and Associates is here to support that process with practical, field-tested services that help hospitals, clinics, and other organizations improve safety and reduce risk.




